3 months ago, we watched a client lose Rs. 20 lakh in potential revenue because their product URLs weren’t compliant with Google’s standards.
Sounds dramatic? It isn’t.
Mrs Sangeeta, home decor brand, had everything right: beautiful handcrafted products, competitive pricing, and even decent SEO. But her Google Merchant Centre kept rejecting products. Why? Her URLs contained characters that violated RFC compliance standards. Something as simple as using spaces instead of hyphens in product URLs.
At Savvytree, we’ve been optimising e-commerce setups for over half a decade, and this scenario happens more often than you’d think. The frustrating part? Most business owners don’t even realise their URLs are the problem. They assume it’s their product descriptions or pricing that’s causing disapproval.
Google Merchant Centre URL compliance isn’t just technical bureaucracy; it’s the foundation that determines whether your products actually reach customers. Get it wrong, and you’re invisible. Get it right, and you’ve got a direct pipeline to millions of shoppers actively looking for what you sell.
What Google Merchant Centre Actually Does?
In Simple words, schema markup is a type of code that you add to your website to help Google understand what your webpage content is about, not just what’s there on the page. Imagine you have a webpage about a restaurant. Without schema markup, Google see it as just a bunch of words and images. But with schema, you can actually tell Google,
“Hey, this is a restaurant, here’s its address, its opening hours, the menu, and even customer ratings.”
It’s like giving search engines a detailed map to navigate your website better.
This extra layer of information is called “structured data.” Schema markup turns your content into a clear, machine-readable format that search engines can easily digest. That’s why when you search for something on Google, you might see rich snippets, those eye-catching results that show stars, prices, or event dates. These come from schema markup.
Why Schema Markup is Important for SEO in 2025
Here’s what most people get wrong about GMC.
They think it’s just another advertising platform. Wrong. Google Merchant Centre is actually the data hub that feeds your product information to every corner of Google’s ecosystem, Search, Shopping, Images, Maps, and even YouTube. Without it, you’re basically invisible to online shoppers.
After setting up hundreds of these accounts, we can tell you the biggest misconception: people assume it’s complicated. It’s not. Well, the setup isn’t complicated. The optimisation part? That’s where things get tricky.
GMC operates on a simple principle: you upload your product data, Google validates it, and then displays it across its network. But here’s the catch, and why we still have a job, Google’s validation process is ruthless. One wrong character in your URL structure and boom, product disapproved.
The platform itself is free. Always has been, always will be. You pay for the ads that come afterwards, but the basic functionality of listing your products costs nothing. That’s Google’s genius move, really. Get merchants hooked on free visibility, then charge them for premium placement.
What makes or breaks your success isn’t understanding what GMC does; it’s understanding what it demands. And at the top of that list? Clean, compliant URLs.
The URL Compliance Crisis Nobody Talks About
Why do 40% of new GMC accounts get disapproved within their first month?
URLs. That’s it. Not product descriptions, not pricing, not even image quality. It’s the URLs that kill most merchants before they ever get started.
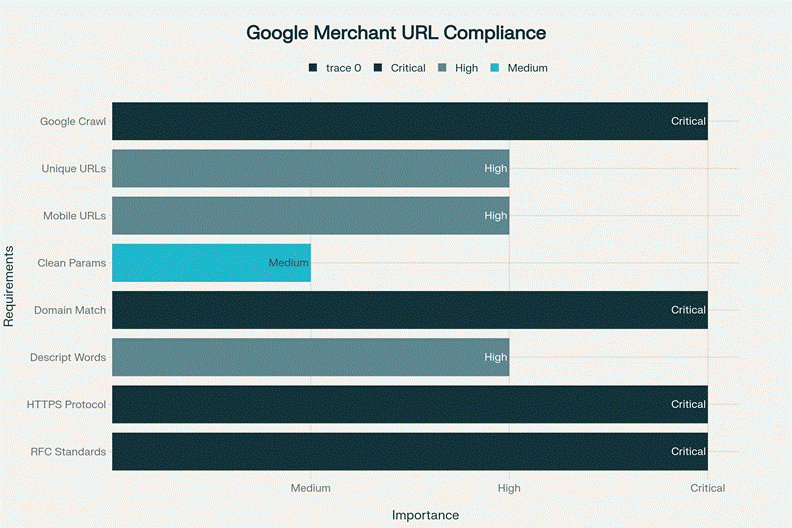
Look, here’s the thing nobody wants to admit: Google’s documentation on URL requirements is scattered across 17 different help pages. we’ve counted. They mention RFC 2396 compliance in passing, but what does that actually mean for someone trying to sell handcrafted home decor? Most people have no clue.
Last year, we audited a pet accessory brand that’d been struggling with GMC for 6 months. Their products kept getting flagged, support tickets went nowhere, and they were ready to give up entirely. The problem? Their URLs contained ampersands without proper encoding. Five minutes of URL cleanup, and suddenly, they had all products approved overnight.
This isn’t rare. It’s epidemic.
The frustrating part is how preventable these issues are. Google’s algorithms don’t care about your intentions; they see non-compliant URLs and automatically flag them. No human review, no appeal process, just rejection. You fix the URL or your product stays invisible.
What’s worse, most e-commerce platforms generate URLs that technically work for web browsing but violate GMC standards. Shopify, WooCommerce, and Magento all have default settings that’ll get you in trouble with Google’s validators. The platforms know this, but fixing it isn’t their priority.
Meanwhile, your competitors with clean URLs are capturing sales you should be getting.
Step-by-Step URL Optimisation Process
Let me walk you through exactly how we handle this for clients.
Step 1: Audit Your Current URLs
Start with a brutal assessment. Export your product feed and scan for these red flags: spaces, special characters (!@#$%), non-ASCII characters, and URLs longer than 2,000 characters. we use a simple spreadsheet formula to catch most issues, but honestly? Manual review finds problems automated tools miss.
Step 2: Fix the Format Structure
Your URLs must follow this pattern: https://yourdomain.com/category/product-name
Notice the hyphens, not underscores. Google prefers hyphens for word separation. Also, keep everything lowercase. Mixed case URLs work fine for browsers but can confuse GMC’s validators.
Step 3: Handle Product Variants Properly
This trips up everyone. Each product variant needs its own unique URL. So if you’re selling a t-shirt in red, blue, and green, you need three separate URLs: /t-shirt-red, /t-shirt-blue, /t-shirt-green. Don’t use query parameters like ?color=red; GMC doesn’t handle them consistently.
Step 4: Clean Up Special Characters
Ampersands become %26. Spaces become %20 or hyphens. Apostrophes? Just remove them entirely. we learned this the hard way when a client’s “men’s shoes” category kept failing because of that apostrophe.
Step 5: Test URL Accessibility
Before uploading anything to GMC, test each URL manually. Can you access the product page? Does it load properly on mobile? We’ve seen merchants submit URLs that worked fine on desktop but threw 404 errors on mobile browsers.
Step 6: Validate Against RFC Standards
Use Google’s own URL inspection tool in Search Console. If it can crawl and index your URLs, GMC will accept them. This step typically takes 2-3 hours for a catalogue of 500 products, but it’s worth every minute.
Step 7: Upload and Monitor
Submit your cleaned feed to GMC, then watch the diagnostics tab obsessively. We check it 3 times daily for the first week after any URL changes. Issues surface quickly, and early detection saves weeks of troubleshooting later.
Pro tip from the trenches:
Keep a backup of your original URLs before making changes. We once had a client whose entire website broke because their developer implemented URL changes without proper redirects. We rolled back in twenty minutes instead of losing a weekend.
The whole process takes most merchants about a week if they’re methodical about it.
Advanced Troubleshooting
The tricky stuff most guides won’t tell you about.
Scenario 1: Canonical URL Conflicts
When your product appears on multiple category pages, GMC gets confused about which URL to use. We encountered this nightmare with a home decor retailer who had the same cow heads/horse heads listed under “wall decor,” “Decor Accent,” and “Gifts.” Solution? Pick one primary URL and add canonical tags pointing to it from all other versions.
Scenario 2: Dynamic Parameter Issues
Some platforms generate session IDs or tracking parameters automatically. Your URL might look clean, but behind the scenes, it’s adding ?sessionid=12345 to everything. These URLs work fine for users, but GMC treats each variation as a different product. Took us 3 days to figure this out for a client because their platform documentation was completely wrong about how to disable it.
Scenario 3: SSL Certificate Mismatches
Your HTTPS URLs might return valid pages, but if your SSL certificate doesn’t cover all subdomains, GMC throws cryptic “unreachable” errors. This bit me hard with a multi-brand client who had separate subdomains for each brand but only covered the main domain in their SSL certificate.
When to use automated tools versus manual fixes?
Automated tools work great for bulk URL formatting, but they can’t solve logic problems or platform-specific quirks. I still manually review anything involving more than basic character replacement.
Also Read: What Is Looker Studio, and Why is It Essential for Digital Marketing Reports
How to Contact Google Merchant Centre Support
We’ve contacted GMC support dozens of times over the years, so here’s what actually works.
The Help Center is your first stop, but don’t expect miracles. It covers about 60% of common issues. For URL problems specifically, search for “link attribute” or “website URL” rather than generic terms like “product disapproved.”
Phone support doesn’t exist for GMC. Period. Don’t waste time looking for it.
Your best bet?
The community forums. Seriously. Google’s product experts monitor these daily, and we’ve gotten faster responses there than through official channels. Post your specific error message, include screenshots, and someone usually responds within 24 hours.
Chat support through Google Ads works if you’re running paid campaigns. They can escalate GMC issues, though they’ll try to redirect you first.
Small Business Advisors offer free consultations if you qualify. We’ve used this service for three clients facing complex disapprovals. Success rate? About 70%, but they actually understand technical URL issues unlike general support.
Prepare your merchant ID, error screenshots, and specific URLs before contacting anyone.
Conclusion
Remember Sangeeta from the beginning?
After we fixed her URL structure, her disapproval rate dropped from 85% to less than 3% within 2 weeks. Those 20 Lakhs in lost sales? She recovered that in the first month after the fix.
Google’s getting stricter with URL compliance, not more lenient. The rollout of Merchant Centre Next means even tighter integration between Google Merchant Centre (GMC) and Google’s broader ecosystem. URLs that pass today might not pass tomorrow.
Your immediate action: audit 5 of your top-selling products right now. Check their URLs against the steps we outlined above. If you find issues, fix them before uploading your next product batch.
Here’s what keeps me curious, though: if something as simple as URL structure can make or break your entire Google Shopping strategy, what other “minor” technical details are we all overlooking?